1.1 - Pointer, Array and Introduction to Data Structure - 2101702130 - Andrean
Pertemuan ke-1
20-02-2018
Array
- A collection of similar
data elements
- These data elements have
the same data type (homogenous)
- The elements of the array
are stored in consecutive memory locations and are
referenced by an Index
- Array index starts from zero (0)
Array Declaration & Accessing Array
- One
Dimensional Array
Syntax : type name[size];
Example :
Delcaration :
int arr[5];
int arr[5];
Accessing:
- arr[0] = 2;
- arr[1] = 5;
- arr[2] = 1;
- arr[3] = 3;
- arr[4] = 4;
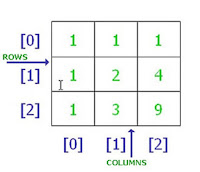
- Two Dimensional Array
Syntax : type name[size 1][size 2];
Example :
Delcaration :
int arr[5][5];
int arr[5][5];
Accessing:
- arr[0][2] = 1;
- arr[2][1] = 1;
- arr[1][2] = 2;
- arr[2][2] = 9;
- Multi Dimension Array
Syntax : type name[size 1][size 2][size 3][size...];
Example :
Declaration :
int arr[4][3][7][10];
Accessing:
- arr[0][2][2][9]= 2;
- arr[2][1][6][0]= 9;
- arr[3][0][0][6]= 13;
- arr[2][1][3][8]= 10;
note : there is no limit index of array at Multi Dimensional Array.
Operations in Array
- Traversal
- Insertion
- Searching
- Deletion
- Merging
- Sorting
Pointer
is a data type whose value refers to another value stored
elsewhere in computer memory using its address.
two important operators used with pointer :
& the address operator
* the dereferencing operator
Declration :
Example :
int a = 10;
int *p = &a;
printf( " %d\n ", *p );
outcome : 10
- int x;
- int *px;
Example :
int a = 10;
int *p = &a;
printf( " %d\n ", *p );
outcome : 10
Single Pointer vs Double Pointer
int a= 17; // let location be 1000
int *ptr,**ddptr; // creates two pointers let ptr have location 3000 and ddptr has location 4000.
ptr=&a; // ptr is initialized with address of a which is 1000
ddptr=&ptr; // ddptr is initialized with address of address of ptr which is 3000. so ddptr contains 3000.
*ddptr; // gives output as value in the location pointed by ddptr. so it have value as 1000.b
**ddptr ; will give 17, first it takes *ddptr it is 1000, then it takes *1000 that is 17.
this called double pointer.
source : https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-the-single-pointer-and-double-pointer
note : you can use as many levels of pointers as you want.
Data Structure
is an arrangement of data, either in the computer’s memory or on the disk storage.
Example :
- Arrays
- Linked lists
- Queues
- Stacks
- Binary trees
- Hash tables
Data Type
is a collection of objects and a set of operations that act on those objects.
Example :
data type int consist :
- Object : 1, 10, 100, etc
- Operations : +, -, /, etc
predefined data :
- int
- char
- float
- etc
Abstract Data Type
(ADT) is a data type that is organized in such a way that the specification of the objects and the specification of the operations on the objects is separated from the representation of the objects and the implementation of the operations.
2101702130 - Andrean







Komentar
Posting Komentar